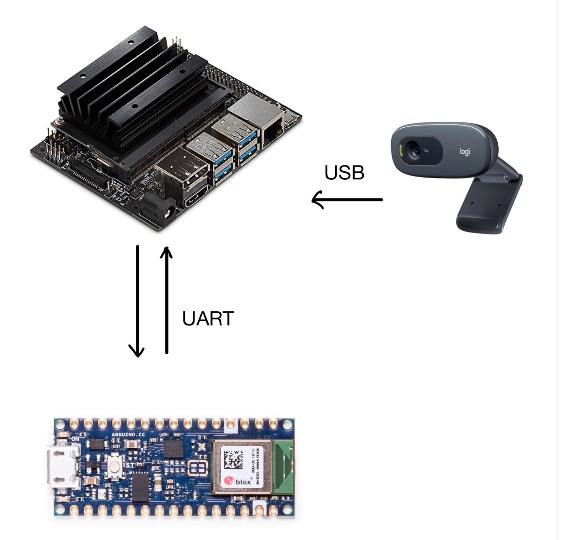
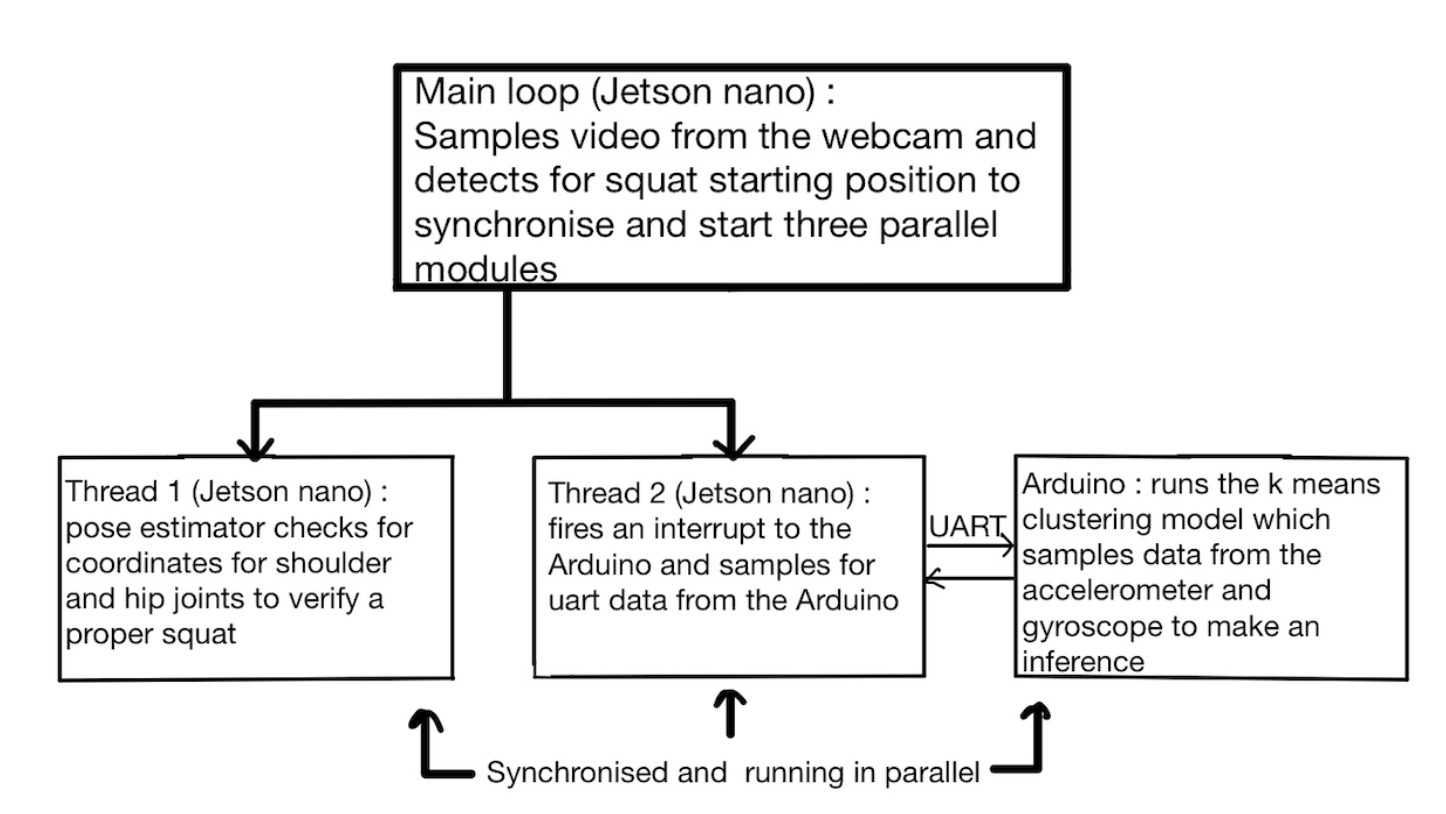
The goal of our project is to use cutting-edge computer vision techniques in combination with embedded devices to help people improve their exercise form while also prioritizing their health and safety. While modern computer vision algorithms are able to detect a person’s pose with impressive accuracy, they often lack the ability to assess depth or provide comprehensive feedback from a single angle. To address this limitation and create a more robust system, we’ve incorporated anomaly detection using embedded devices that are worn by the user during their workout. These devices monitor rotation angles and motion acceleration to ensure that we can provide accurate feedback and help users optimize their form, while also minimizing the risk of injury. By combining data from multiple sources, we aim to create a powerful tool that can assist people in achieving their fitness goals with confidence and peace of mind.
To demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, we have chosen squats as the primary exercise to focus on. Squats are a fundamental exercise that targets multiple muscle groups, making it an excellent choice for our project. However, performing squats incorrectly can lead to serious injuries, making it a high-risk exercise for beginners and experienced individuals alike. Through our project, we hope to show the potential of this technology to support users in achieving their fitness goals while promoting safe and effective exercise practices.